10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Non Woven Fabric for Your Projects
In the ever-evolving world of textile innovation, selecting the right material is crucial for achieving successful project outcomes. Among the myriad of options available, non woven fabric stands out due to its versatility and functionality. According to Dr. Emily Hargrove, a leading expert in textile engineering, "The selection of non woven fabric can significantly impact the durability and performance of your products." This statement emphasizes the importance of making informed choices when considering non woven fabrics for various applications.
As more industries recognize the benefits of non woven fabric, understanding its properties becomes essential for designers and manufacturers alike. Factors such as weight, absorbency, and ecological impact should be considered, as they can greatly influence the final product's performance. With a plethora of options on the market, this guide aims to provide ten essential tips that will help you navigate the intricacies of choosing the best non woven fabric for your projects, ensuring that you make selections that not only meet your specific needs but also contribute positively to sustainability efforts in the textile industry.

Understanding Non Woven Fabric: Types and Characteristics
Non-woven fabrics have gained significant traction across various industries due to their unique characteristics and versatility. These fabrics are made from a combination of fibers bonded together through chemical, mechanical, or thermal processes, distinguishing them from traditional woven textiles. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global non-woven fabric market is projected to reach USD 50.28 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.0%. This rapid growth is indicative of the material's increasing application in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and construction.
When choosing the best non-woven fabric for your projects, understanding the types and their respective characteristics is crucial. Non-woven fabrics can be categorized into several types, including spunbond, meltblown, and needlepunch, each offering unique properties. Spunbond fabrics, known for their strength and durability, are commonly used in the production of bags, while meltblown fabrics are highly effective in filtration applications due to their fine fiber diameter. Furthermore, needlepunch fabrics provide excellent abrasion resistance, making them ideal for clothing and upholstery. By identifying the specific needs of your project and the characteristics of available non-woven materials, you can ensure the optimal fabric selection that meets both performance and budgetary criteria.
Comparison of Non-Woven Fabric Types
Factors to Consider: Weight, Thickness, and Durability
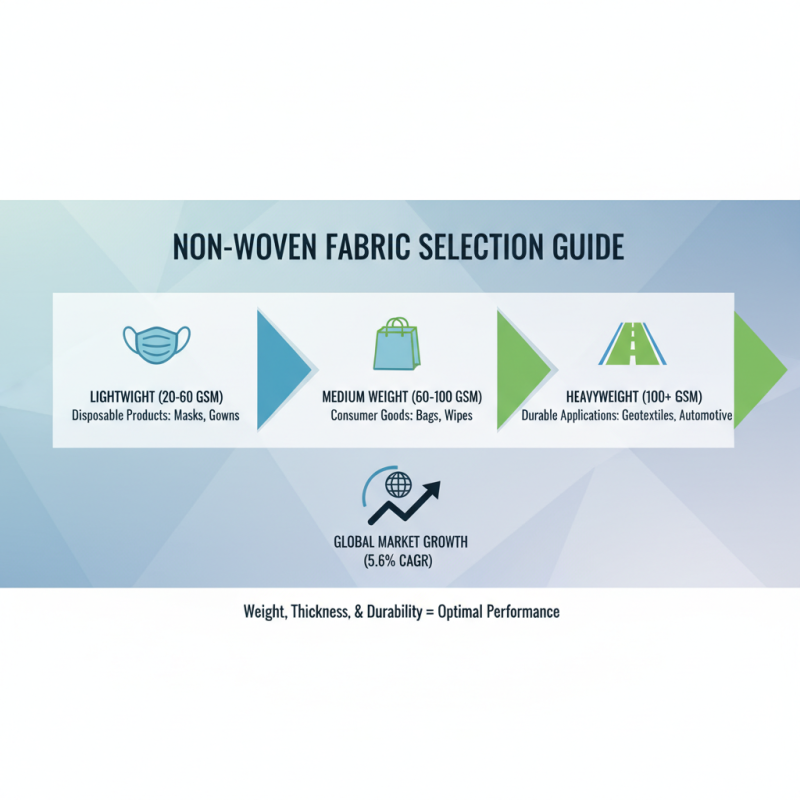
When selecting non-woven fabric for various projects, weight, thickness, and durability are crucial factors that can significantly affect the end product's performance and usability. The weight of non-woven fabric, often measured in grams per square meter (gsm), determines its strength and application suitability. Lightweight non-woven fabrics, typically ranging from 20 to 60 gsm, are ideal for disposable products such as masks and surgical gowns, while heavier options above 100 gsm are better suited for more durable applications like geotextiles and automotive interiors. According to a report by the Nonwovens Institute, the global nonwoven market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6%, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right weight for optimal usage.
Thickness is another essential attribute, as it influences both the fabric's tactile feel and its overall structural integrity. Generally, thicker non-woven fabrics exhibit enhanced durability and puncture resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Reports indicate that advancements in non-woven technology have led to products with varying thicknesses, with some fabrics reaching up to 5 mm, providing better protection and longevity. Understanding the specified thickness necessary for your project will not only ensure functional efficacy but also contribute to aesthetic quality and user satisfaction.
Durability, a vital characteristic of non-woven fabrics, reflects their ability to withstand wear and tear in practical applications. Factors leading to enhanced durability include fiber composition and bonding techniques. Non-woven fabrics produced with advanced thermal or chemical bonding methods show promising results, exhibiting a tensile strength improvement of up to 30% compared to traditional methods, as highlighted in the latest market analysis by Freedonia Group. For projects requiring robust and long-lasting materials, prioritizing durability alongside weight and thickness becomes paramount to meet performance expectations while ensuring safety and reliability in application.
Assessing Fabric Composition: Natural vs. Synthetic Materials

When selecting the best non-woven fabric for your projects, understanding the fabric composition is crucial. Non-woven fabrics can be made from a variety of materials, primarily falling into two categories: natural and synthetic. Natural fibers, such as cotton or jute, offer breathability, biodegradability, and a soft texture. However, they may not provide the same durability or water resistance as some synthetic options. On the other hand, synthetic materials like polypropylene and polyester are known for their strength, resistance to moisture, and ability to retain their shape over time.
One important tip is to evaluate the purpose of your project. For instance, if you’re creating items that will be frequently washed or exposed to moisture, leaning towards synthetic non-woven fabrics may be a smart choice due to their durability and moisture-wicking properties. Conversely, if your project prioritizes sustainability or a natural look and feel, natural fibers might be more appropriate.
Another factor to consider is the weight and thickness of the fabric. Denser fabrics often provide better protection and structure, making them ideal for applications like tote bags or protective covers. Make sure to assess the weight in relation to your project's requirements. A lighter weight material might suffice for items that don’t require high durability, while heavier fabrics could be necessary for robust products. Understanding these differences will lead to a more informed decision in your fabric selection process.
Application-Specific Requirements: Selecting the Right Fabric
When selecting a non-woven fabric for specific applications, it is crucial to consider characteristics such as strength, durability, and absorbency. Non-woven fabrics, produced through various methods like thermal bonding or chemical treatments, display a wide range of physical properties. According to a report by Technavio, the global non-woven fabric market is expected to grow by $25.5 billion from 2021 to 2025, indicating a rising demand for these versatile materials. For instance, spunbond non-woven fabrics are known for their high tensile strength and are widely used in agricultural applications, while meltblown fabrics, often employed in filtration and hygiene products, provide superior absorbency due to their fine fiber structure.
Another key factor in choosing the right non-woven fabric is understanding the specific requirements of your project. In medical applications, for example, the fabric must meet stringent standards for bacteria filtration and liquid repellency, with the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) guidelines providing a foundation for testing criteria. With the projected growth of the hygiene products market, which is pushing towards a more sustainable direction, materials such as biodegradable non-woven fabrics are increasingly favored in product design, accommodating both environmental concerns and functionality. It is essential for manufacturers and designers to keep these application-specific requirements in mind to ensure the chosen fabric not only meets performance expectations but also complies with industry standards.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Non Woven Fabrics
The sustainability and environmental impact of non-woven fabrics are becoming increasingly important as the demand for eco-friendly materials rises. Non-woven fabrics, made from synthetic or natural fibers, can be designed with various properties suited for diverse applications, ranging from medical supplies to household items. When choosing a non-woven fabric, it's essential to consider its life cycle and how it affects the environment. Many non-woven options are crafted from recycled materials, reducing waste and the resources needed for production. Additionally, they often require less energy in manufacturing than traditional woven fabrics, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
Another critical aspect of sustainability is the biodegradability of non-woven fabrics. Many of these materials can break down over time, especially those made from natural fibers like cotton or jute. However, synthetic non-woven fabrics, like those made from polypropylene, present challenges due to their longevity in landfills. When selecting non-woven fabrics for projects, opting for biodegradable alternatives or those made from recycled materials significantly reduces environmental impact. Furthermore, fostering awareness of the disposal practices for these products can enhance their sustainability. Making informed choices about non-woven fabrics not only supports environmentally responsible practices but also fosters a broader culture of sustainability in the textile industry.
10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Non Woven Fabric for Your Projects - Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Non Woven Fabrics
| Tip No. | Tip Description | Environmental Impact | Durability | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Assess fabric composition | Biodegradable options reduce landfill waste | Good for short-term use | Packaging materials |
| 2 | Consider thickness and weight | Thicker non wovens might use more resources | Highly durable | Reusable bags |
| 3 | Evaluate manufacturing processes | Eco-friendly processes lower carbon footprint | Varying levels of durability | Medical and hygiene products |
| 4 | Check for certifications | Certifications can indicate sustainable practices | Generally durable, depends on grade | Home textiles |
| 5 | Look into color options | Dyes can have harmful environmental effects | Colorfast and durable | Decorative uses |
| 6 | Determine proper care guidelines | Improper disposal can be harmful | Maintenance affects lifespan | Reusable covers |
| 7 | Analyze its tensile strength | Strong materials help with waste reduction | Very durable | Industrial applications |
| 8 | Evaluate moisture resistance | Helps prevent mold and waste | Varied moisture resistance | Outdoor uses |
| 9 | Seek user feedback | Real-world data on environmental impact | Various durability reports | Consumer products |
| 10 | Plan for end-of-life scenarios | Promotes recycling and circular economies | Long-lasting options available | Sustainable fashion items |
Related Posts
-

Top 2025 Uses and Benefits of Non Woven Fabric You Need to Know
-
What is Non Woven Fabric and How is it Used in Everyday Products
-

How to Choose the Best Non Woven Fabric for Your Projects
-

Why Non Woven Fabric is Revolutionizing Industries and Everyday Products
-

Why Non Woven Fabric Manufacturers Are Key to Sustainable Industry Solutions
-

What is Non Woven Textile Manufacturers and Their Key Benefits for Businesses