What is a Non-Woven Cloth Making Machine and How Does It Work?
The non-woven cloth industry has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, largely driven by innovations in technology, particularly in the area of manufacturing equipment. A non woven cloth making machine plays a pivotal role in this transformation, enabling the production of a wide range of materials utilized in various sectors, including healthcare, automotive, and personal care products. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in textile manufacturing, "The non woven cloth making machine revolutionizes the way we produce fabrics, allowing for greater efficiency and versatility than ever before."
As the demand for sustainable and efficient textile solutions continues to rise, understanding the operation and capabilities of a non woven cloth making machine becomes increasingly important. These machines utilize processes such as spunbonding, needlepunching, and hydroentangling to create fabrics without traditional weaving methods. This not only streamlines production but also reduces waste, making it a key player in the push towards environmentally conscious manufacturing. With experts like Dr. Carter emphasizing the significance of these machines, it is clear that their impact on the industry will only grow in the coming years, marking a shift in how we think about fabric production.
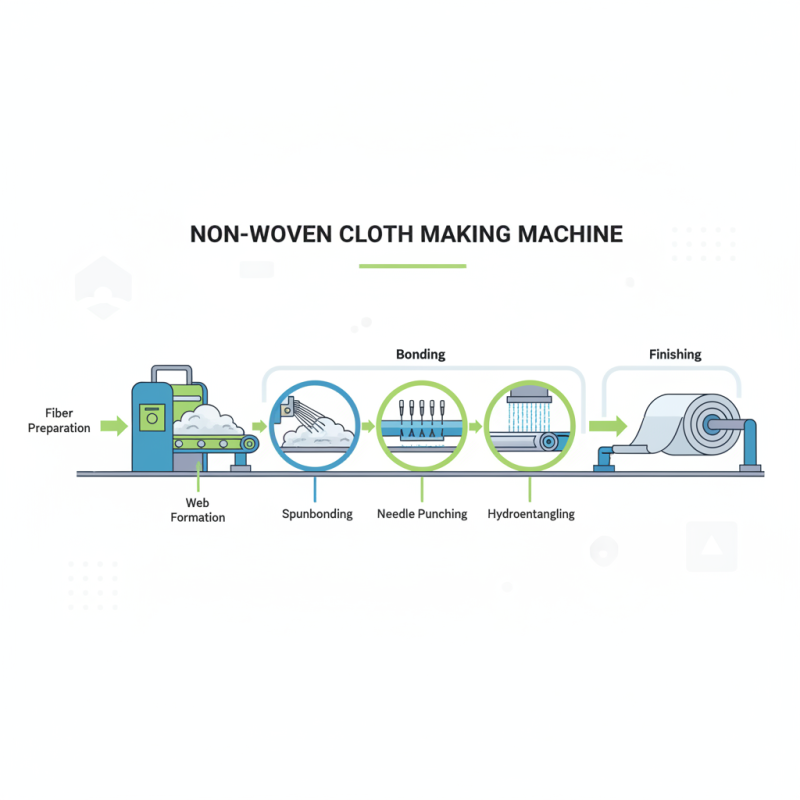
What is a Non-Woven Cloth Making Machine?
A non-woven cloth making machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed for producing non-woven fabrics, which are versatile materials utilized in a variety of applications. Unlike woven fabrics that are made by weaving threads together, non-woven fabrics are created through the bonding of fibers, offering distinct advantages such as cost-effectiveness, lightweight construction, and enhanced durability. This machine operates by employing several processes, including carding, laying, and bonding, to transform raw fibers into a finished product.
During the manufacturing process, fibers, often derived from natural or synthetic sources, are first carded into a loose web. This web is then laid out in specific patterns and subjected to bonding methods like thermal, mechanical, or chemical treatments to solidify the material. The result is a non-woven fabric that can be further processed or finished according to specific requirements, making it suitable for applications in industries ranging from hygiene products to medical supplies and geotextiles. The non-woven cloth making machine plays a crucial role in modern textile production, offering flexibility and efficiency to meet the growing demand for diverse fabric solutions.
Non-Woven Cloth Production vs. Traditional Fabric Production
This chart compares the production output of non-woven cloth making machines versus traditional fabric production methods over a span of five years. The data reflects the growing adoption of non-woven technology in the textile industry.
Types of Non-Woven Cloth Making Machines
Non-woven cloth making machines play a crucial role in the textile industry, producing a variety of non-woven fabrics used in applications ranging from hygiene products to industrial materials. There are several types of non-woven cloth making machines, each designed to produce specific fabric characteristics and meet diverse end-user needs.
One common type is the spunbond machine, which creates non-woven fabrics by extruding molten polymer through spinnerets to form continuous filaments. These filaments are then laid down on a conveyor belt and bonded using heat and pressure, resulting in a strong, durable textile.
Another popular option is the meltblown machine, which employs a similar process but uses high-velocity air to stretch the filaments, creating a finer, more porous fabric ideal for filtration and absorbent products.
Additionally, there are needle-punching machines, which utilize barbed needles to entangle fibers together, creating a dense fabric with a textured surface, commonly used in automotive carpets and geotextiles.
Other types include hydroentangling machines that use high-pressure water jets to bond fibers, providing a soft and absorbent fabric suitable for wipes and medical applications. Each of these machines utilizes distinct processes and technology, catering to the varied requirements of non-woven fabric production.
Key Components of Non-Woven Cloth Making Machines
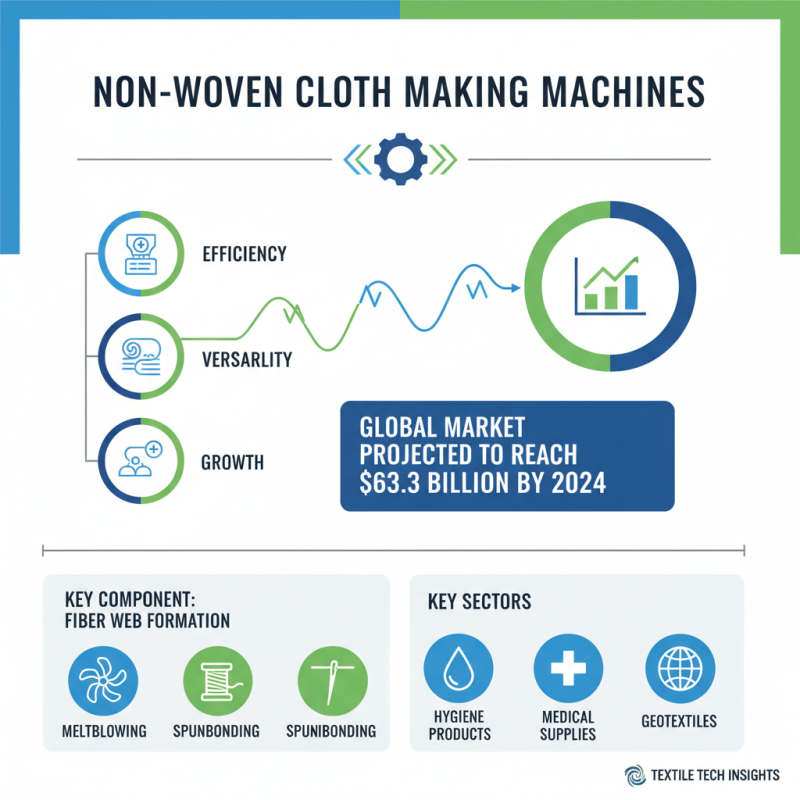
Non-woven cloth making machines play a vital role in the fast-evolving textile industry, particularly due to their efficiency and versatility. A key component of these machines is the fiber web formation unit, which can involve several methods such as meltblowing, spunbonding, or needle punching. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global non-woven fabrics market is projected to reach USD 63.3 billion by 2024, underscoring the significance of these machines in producing materials that meet increasing demand across various sectors, including hygiene products, medical supplies, and geotextiles.
Another essential component of non-woven cloth making machines is the bonding technology utilized, which is critical for determining the final properties of the fabric. Techniques such as thermal bonding, chemical bonding, and mechanical bonding are commonly employed. Each method offers unique advantages depending on the intended application of the non-woven fabric. For instance, thermal bonding is prevalent in applications requiring lightweight and flexible materials. Market analysis shows that the thermal bonding segment accounted for approximately 40% of the total non-woven bonding technologies in 2020, highlighting its importance in the industry. These components work in unison to produce high-quality non-woven materials that are crucial for modern applications.
The Process of Making Non-Woven Cloth
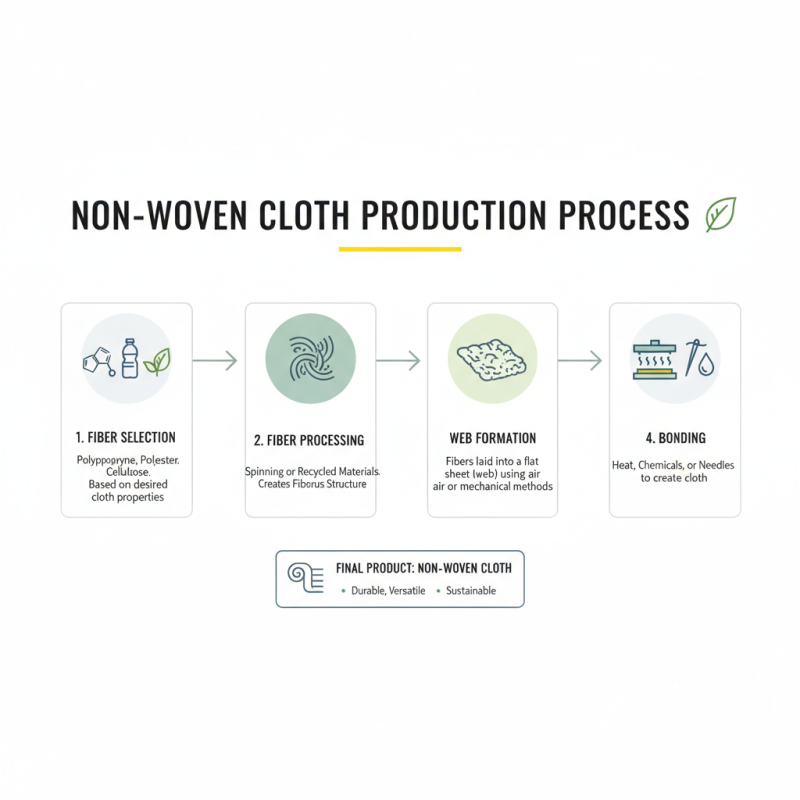
The process of making non-woven cloth involves several key steps that transform raw materials into the final product. Initially, fibers are selected based on the desired properties of the cloth. Common choices include polypropylene, polyester, and cellulose, which are processed into a fibrous structure. These fibers can be produced through various methods such as spinning, or they can come from recycled materials, promoting sustainability.
Once the fibers are acquired, they are laid out in a mat-like formation. This mat is then bonded together using one of several techniques. The most prevalent methods include thermal, chemical, or mechanical bonding. In thermal bonding, heat is applied to melt certain fibers at their points of contact, effectively fusing them together. Chemical bonding utilizes adhesives to achieve a similar effect, while mechanical bonding involves entangling the fibers through needle punching or water jet processes.
Tips: When choosing materials for non-woven cloth, consider the end-use to ensure suitability. For example, fabrics intended for medical applications should prioritize hygiene and barrier properties. Additionally, always check for sustainability certifications if environmental impact is a concern, as many manufacturers now offer eco-friendly options that use recycled materials or low-impact processes.
Applications and Benefits of Non-Woven Cloth Products
Non-woven cloth products have gained significant traction across various industries due to their versatility and unique properties. These materials are made from fibers that are bonded together through chemical, mechanical, or thermal processes, allowing for a range of applications. One of the primary uses of non-woven cloth is in the medical field, where it serves as a critical component in surgical masks, gowns, and other protective garments. The ability to create lightweight, breathable, and disposable items makes non-woven fabrics an ideal choice for maintaining hygiene in healthcare settings.
Another prevalent application of non-woven cloth is in the construction and home improvement sectors. These fabrics are often utilized for insulation, geotextiles, and roofing materials due to their durability and resistance to moisture. The ease of integration with other materials allows for enhanced performance in various building applications. Additionally, non-woven cloth is increasingly used in household items, such as cleaning wipes, filters, and furniture upholstery, which adds convenience while promoting environmental sustainability through the use of recyclable materials. The overall benefits of non-woven cloth products include cost-effectiveness, lightweight characteristics, and customization options to suit specific needs across multiple industries.
What is a Non-Woven Cloth Making Machine and How Does It Work? - Applications and Benefits of Non-Woven Cloth Products
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine Type | Hydroentanglement, Needle Punching, Melt Blown |
| Production Rate | 100 to 500 kg per hour |
| Fabric Weight | 30 to 150 g/m² |
| Applications | Medical, Hygiene, Agriculture, Geotextiles, Packaging |
| Benefits | Cost-effective, Versatile, Lightweight, Good Barrier Properties |
| Material Types | Polypropylene, Polyester, Viscose, Biodegradable Materials |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced Waste, Recyclable Options Available |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Non Woven Fabric Making Machine Trends and Insights
-

2025 Top 10 Airlaid Nonwoven Products Transforming the Hygiene Industry Landscape
-

What is Nonwoven Industry: Insights into Its Growth and Applications
-
Top Non Woven Fabric Suppliers You Need to Know for Your Business
-

Why Non Woven Fabric Manufacturers Are Key to Sustainable Industry Solutions
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Non Woven Cutting Machine for Your Needs