What is Non Woven Fabric and How is it Used in Everyday Products
Non woven fabric has gained significant popularity for its versatility and practicality in various applications. Defined as a fabric-like material made from fibers bonded together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes, non woven fabric differs from traditional woven or knitted textiles. This unique structure allows it to exhibit distinct properties such as strength, flexibility, and absorbency, making it ideal for a multitude of everyday products.
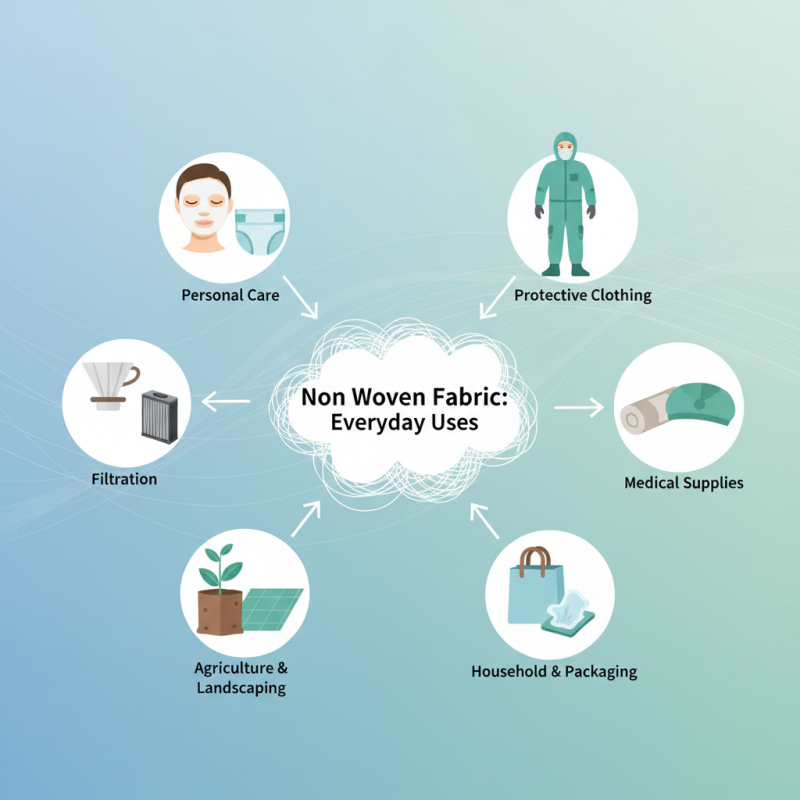
In our daily lives, non woven fabric can be found in an array of items ranging from personal care products like facial masks and diapers to industrial applications such as protective clothing and filtration materials. Its lightweight and breathable nature, combined with the ability to be produced in large quantities, has led to increased adoption across diverse sectors. As we explore the various uses and benefits of non woven fabric, we will uncover how this innovative material contributes to modern convenience while addressing specific functional needs.
Definition and Characteristics of Non Woven Fabric
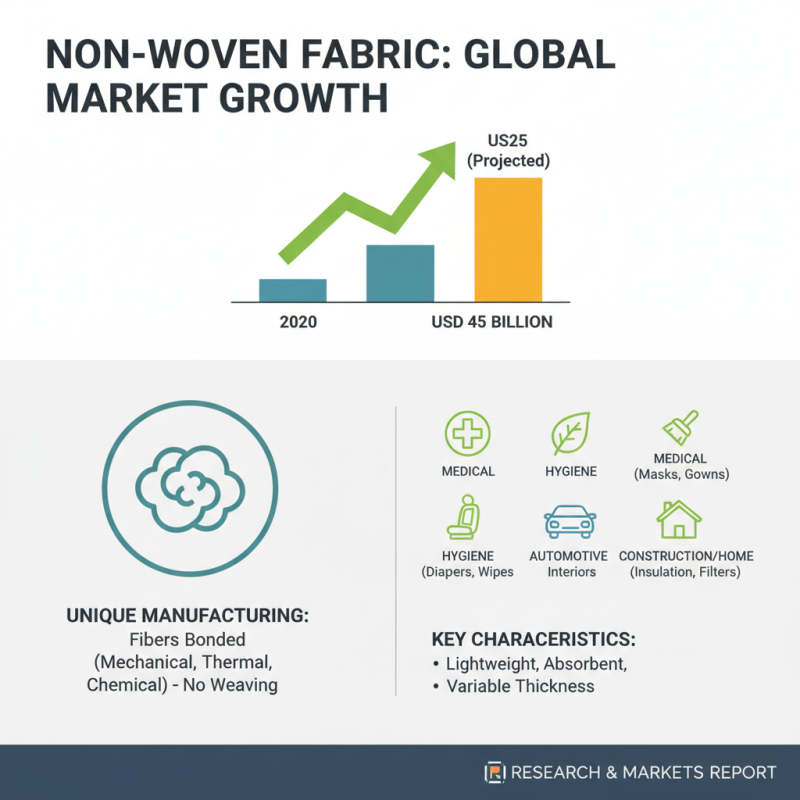
Non woven fabric is a versatile material characterized by its unique manufacturing process, which differs significantly from traditional woven or knitted textiles. It is created by bonding fibers together, typically through mechanical, thermal, or chemical means, without the need for weaving looms. This results in a fabric that is often lighter, more absorbent, and can be produced in various thicknesses, making it ideal for a wide range of applications. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global non woven fabric market was valued at approximately USD 45 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach around USD 60 billion by 2025, reflecting its growing demand across multiple sectors.
The characteristics of non woven fabric include durability, breathability, and cost-effectiveness, which contribute to its popularity in numerous everyday products. For instance, it is commonly used in hygiene products, medical applications, and packaging materials due to its ability to be designed for specific functionalities, such as filtration and liquid resistance. A recent study published in the Journal of Textile Science indicated that non woven fabrics can be engineered to include antimicrobial properties, making them suitable for medical garments and wound dressings. This adaptability not only enhances performance but also drives innovation in product design, as manufacturers continue to explore new uses for non woven materials across industries.
Manufacturing Processes of Non Woven Fabric
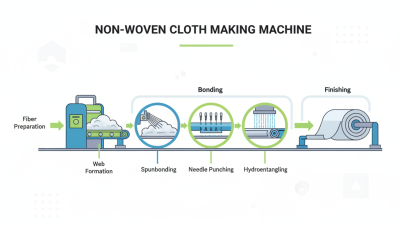
The manufacturing processes of non-woven fabric are diverse and tailored to meet various applications across numerous industries. Non-woven fabrics are produced without the traditional weaving or knitting processes typical of textiles, instead relying on methods that bond fibers together. The most common manufacturing techniques include spunbond, meltblown, and needle punching. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global non-woven fabric market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2022, underlining the significant role these materials play in consumer applications.
Spunbond technology involves extruding molten polymer filaments onto a conveyor belt, where they are simultaneously bonded through a combination of thermal and mechanical means. This process yields strong, lightweight fabrics suitable for applications ranging from medical to geotextile products.
Meanwhile, the meltblown process utilizes high-velocity air to create fine fibers that result in highly absorbent and filter materials, essential for products like face masks and other filtration systems. A recent market analysis indicated that the medical sector accounted for around 25% of the overall non-woven fabric usage in 2023, highlighting the critical role these materials play in healthcare.
Additionally, needle punching involves mechanically entangling fibers, creating sturdy fabrics that are often utilized in carpets and automotive interiors. Each of these techniques contributes to the versatility and functionality of non-woven fabrics, catering to the increasing demand for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials.
The global shift towards sustainability has also prompted innovations in manufacturing practices, with a growing focus on biodegradable and recyclable options, further expanding the non-woven fabric market's potential.
Common Applications of Non Woven Fabric in Everyday Products
Non woven fabrics are an innovative material widely utilized in various everyday products due to their unique properties, including durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global non woven fabrics market size was valued at approximately USD 24 billion in 2020 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is largely driven by the increasing demand in industries such as hygiene, medical, and construction, where non woven fabrics are preferred for their lightweight and moisture-wicking abilities.
In everyday applications, non woven fabrics play crucial roles across multiple sectors. In the hygiene sector, they are extensively used in the production of products like diapers, feminine hygiene items, and adult incontinence products, providing essential absorbency and comfort. The medical field also utilizes non woven materials for surgical gowns, masks, and drapes, where their barrier properties are vital for infection control. Additionally, in the home improvement and agricultural industries, non woven fabrics are increasingly used in landscaping, as weed control fabrics, and as building materials for insulation and soundproofing, showcasing their adaptability and functional benefits across various applications. With the growing emphasis on sustainability, non woven products made from recycled or biodegradable materials are anticipated to gain more traction in the market, further expanding their role in everyday life.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Non Woven Fabrics
Non woven fabrics have gained significant popularity due to their versatility and functionality in various applications, from medical supplies to household items. However, as their usage rises, so does the concern regarding their environmental impact. These fabrics are primarily made from synthetic materials, which can be non-biodegradable and contribute to increasing plastic waste in landfills. Although some non woven products are designed to be disposable, their long-term presence in the environment poses a challenge to sustainability efforts.
To mitigate these challenges, several approaches are being explored to enhance the sustainability of non woven fabrics. Manufacturers are investigating the use of biodegradable materials and recycled fibers, which can reduce the environmental footprint of these products. Additionally, innovations in fabric production techniques aim to optimize resource use, such as energy and water consumption, and minimize pollution during manufacturing. The development of eco-friendly alternatives ensures that while non woven fabrics serve their practical purposes, they can also align with growing environmental preservation goals, fostering a more sustainable future for this vital material.
Usage of Non Woven Fabrics in Everyday Products
This bar chart illustrates the various applications of non woven fabrics in everyday products, showcasing their prevalence in different sectors.
Future Trends in Non Woven Fabric Technology and Usage
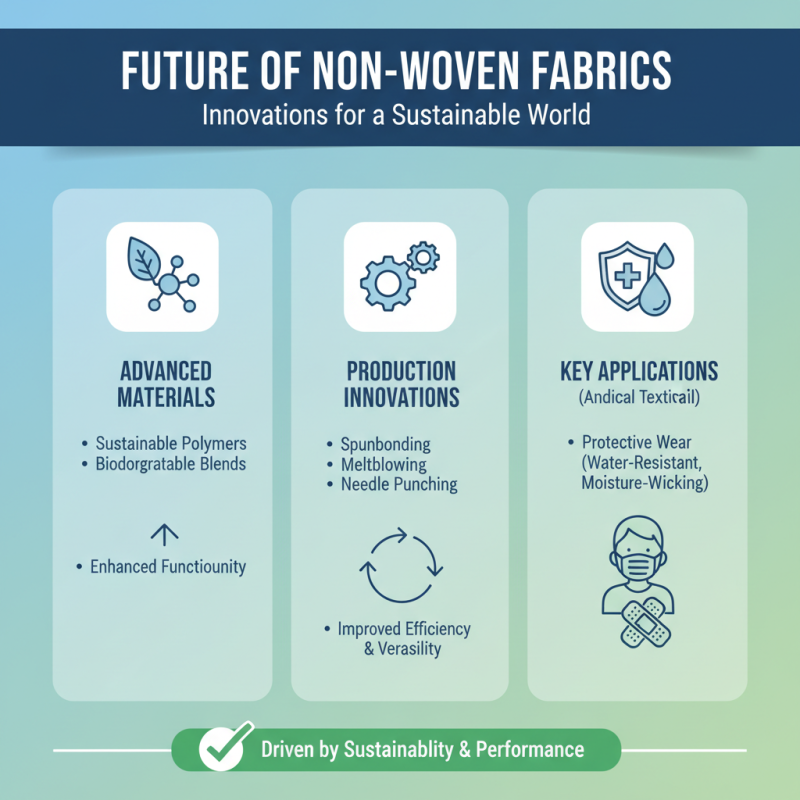
The future of non-woven fabric technology is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in material science and an increasing demand for sustainable products. Innovations in production methods such as spunbonding, meltblowing, and needle punching are enhancing the functionality and versatility of non-woven fabrics. These techniques not only improve the performance characteristics of the fabrics, such as durability and water resistance, but also enable the incorporation of antibacterial and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for various applications from medical textiles to personal protective equipment.
Moreover, the shift towards environmentally friendly practices is shaping the future landscape of non-woven fabrics. Manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable materials and recycling methods to reduce environmental impact. The integration of smart technologies, such as embedded sensors and RFID tags, is also becoming a trend, allowing non-woven fabrics to play a role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. As consumer awareness regarding sustainability grows, the industry is poised to innovate further, tapping into renewable resources and creating products that not only serve practical purposes but also contribute positively to the environment. This forward-thinking approach will likely redefine the usage of non-woven fabrics across multiple sectors, including healthcare, automotive, and home textiles.
Related Posts
-

Why Non Woven Fabric Manufacturers Are Key to Sustainable Industry Solutions
-
What is a Non-Woven Cloth Making Machine and How Does It Work?
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Non Woven Cutting Machine for Your Needs
-

2025 Top Non Woven Fabric Making Machine Trends and Insights
-

What is Nonwoven Industry: Insights into Its Growth and Applications
-

2025 Top 10 Airlaid Nonwoven Products Transforming the Hygiene Industry Landscape